Top 10 Ways To Boost Your Immune System

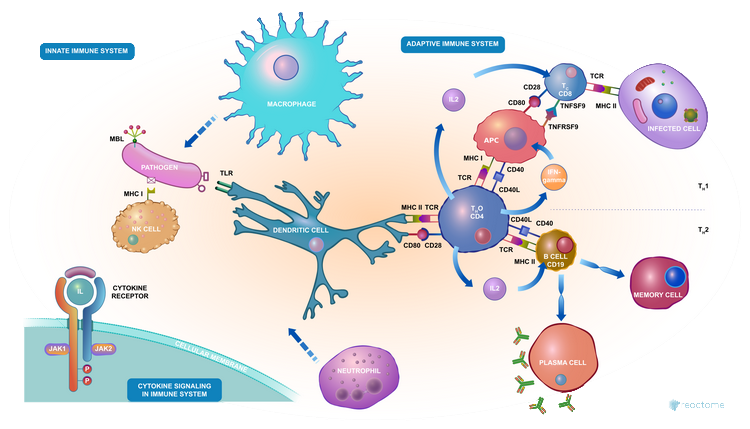
Boosting your immune system is essential for maintaining good health and resilience against infections and diseases. Here’s an in-depth look at ten effective strategies to strengthen your immune system:
1. Maintain a Balanced Diet
A well-rounded diet provides essential nutrients that support immune function. Focus on:
Colorful Fruits and Vegetables: These are rich in vitamins (like vitamin C and E), minerals (such as zinc and selenium), and antioxidants (like beta-carotene) that help combat oxidative stress and support immune cells.
Protein-Rich Foods: Lean meats, poultry, fish, eggs, legumes, and nuts provide amino acids necessary for the synthesis of immune proteins and antibodies.
Healthy Fats: Include sources like avocados, olive oil, nuts, and fatty fish (such as salmon and sardines) that contain omega-3 fatty acids. Omega-3s help reduce inflammation and support immune cell function.
Maintaining a balanced diet is essential for overall health and plays a crucial role in supporting a well-functioning immune system.
2. Stay Hydrated
Proper hydration is crucial for optimal immune function and overall health. Water plays a vital role in:
Toxin Elimination: Adequate water intake helps flush toxins and waste products from the body, supporting kidney function and maintaining a healthy urinary tract.
Nutrient Transport: Water transports essential nutrients, such as vitamins and minerals, throughout the body. These nutrients are critical for immune cell function and maintaining a strong immune response.
Mucous Membrane Health: Well-hydrated mucous membranes in the respiratory and digestive tracts act as barriers against pathogens. They trap potential invaders and prevent them from entering the body.
To ensure adequate hydration, aim to drink at least 8 glasses (about 2 liters) of water per day. Adjust your intake based on factors such as climate, physical activity levels, and overall health status.
3. Get Sufficient Sleep
Quality sleep is essential for immune health, as it allows the body to:
Produce Cytokines: During sleep, the body produces cytokines, which are proteins that play a crucial role in immune signaling and response. These cytokines help regulate inflammation and coordinate the body’s defense against infections.
Support Immune Cell Function: Sleep is also essential for the proper functioning of immune cells, including T cells, which are responsible for recognizing and destroying pathogens.
Repair and Regeneration: Sleep provides an opportunity for the body to repair and regenerate tissues, including those involved in immune function. This regeneration process helps maintain overall health and resilience.
To promote restful sleep, establish a regular sleep schedule by going to bed and waking up at consistent times each day. Create a relaxing bedtime routine, avoid stimulating activities before bed, and ensure your sleep environment is comfortable and conducive to rest.
4. Manage Stress
Chronic stress weakens the immune system and increases susceptibility to infections. Practice stress-reduction techniques such as:
-
Meditation and Mindfulness: These practices promote relaxation and reduce stress hormone levels.
-
Deep Breathing Exercises: Slow, deep breathing activates the body’s relaxation response and helps manage stress.
-
Regular Exercise: Physical activity releases endorphins (natural stress-relievers) and improves mood, which in turn supports immune function
Effectively managing stress is essential for maintaining a strong immune system. Chronic stress can weaken your immune defenses and make you more susceptible to illness.
5. Exercise Regularly
Regular physical activity has numerous benefits for immune health:
-
Enhanced Circulation: Exercise improves blood circulation, allowing immune cells and antibodies to travel more efficiently throughout the body and reach potential infection sites.
-
Reduction of Chronic Inflammation: Regular exercise helps reduce chronic inflammation, which is linked to various diseases and can impair immune function.
-
Stress Reduction: Physical activity stimulates the production of endorphins, neurotransmitters that promote feelings of well-being and reduce stress levels. Lower stress levels contribute to a stronger immune system.
To reap the immune-boosting benefits of exercise, aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity (such as brisk walking, jogging, cycling, or swimming) per week. Additionally, include strength training exercises targeting major muscle groups two or more days per week.
6. Maintain Good Hygiene Practices
Practicing good hygiene habits reduces the risk of infections:
-
Hand Washing: Wash hands frequently with soap and water for at least 20 seconds, especially before eating, after using the restroom, and after coughing or sneezing.
-
Respiratory Etiquette: Cover your mouth and nose with a tissue or your elbow when coughing or sneezing to prevent the spread of germs.Maintaining good hygiene practices is crucial for supporting your immune system and preventing the spread of infections
Maintaining good hygiene practices is crucial for supporting your immune system and preventing the spread of infections.
7. Consider Immune-Boosting Supplements
Certain vitamins and minerals support immune function, although it’s best to obtain nutrients through a balanced diet:
Vitamin C: Found in citrus fruits, strawberries, bell peppers, and broccoli. It helps stimulate the production of white blood cells (immune cells) and antibodies.
Vitamin D: Supports immune regulation and may reduce the risk of respiratory infections. It’s naturally obtained from sunlight and can also be found in fatty fish and fortified foods.
Zinc: Essential for immune cell development and function. Sources include lean meats, shellfish, legumes, nuts, seeds, and whole grains.
Consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplements, as excessive intake can be harmful.
8. Limit Alcohol and Avoid Smoking
Excessive alcohol consumption and smoking have detrimental effects on immune function:
Alcohol: Heavy drinking suppresses the immune system, making it harder for the body to fight off infections. Chronic alcohol use can impair the function of immune cells, disrupt the gut microbiota (which plays a role in immune health), and increase susceptibility to respiratory infections.
Smoking: Tobacco smoke contains harmful chemicals that damage the respiratory system and weaken immune defenses. Smoking compromises lung function, impairs the ability of immune cells to clear pathogens from the airways, and increases the risk of respiratory infections and other diseases.
Limit alcohol consumption to moderate levels—up to one drink per day for women and up to two drinks per day for men—and avoid smoking altogether to support immune health and overall well-being.
9. Maintain a Healthy Weight
Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for immune function and overall health:
-
Inflammation Reduction: Excess body weight, particularly visceral fat (fat stored around organs), contributes to chronic low-grade inflammation. Chronic inflammation can impair immune responses and increase the risk of diseases such as diabetes, heart disease, and certain cancers.
-
Balanced Immune Cell Function: Obesity alters immune cell function and cytokine production, potentially weakening the body’s ability to respond to infections.
To achieve and maintain a healthy weight, focus on:
-
Balanced Diet: Eat a variety of nutrient-dense foods, including fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, whole grains, and healthy fats. Avoid excessive calorie intake from processed foods, sugary beverages, and high-fat snacks.
-
Regular Physical Activity: Engage in regular exercise to burn calories, build muscle, and support overall metabolic health. Combining aerobic exercise with strength training helps maintain muscle mass and promote fat loss.
-
Behavioral Changes: Adopt healthy lifestyle habits, such as mindful eating, portion control, and stress management, to support long-term weight management and immune health.
Maintaining a healthy weight is a key component of overall well-being and plays a significant role in supporting a robust immune system.
10. Stay Up-to-Date with Vaccinations
Vaccinations are critical for protecting against infectious diseases and boosting immune defenses:
-
Preventative Measures: Vaccines stimulate the immune system to produce antibodies against specific pathogens without causing illness. They help prevent infections and reduce the severity of diseases if exposure occurs.
-
Herd Immunity: By getting vaccinated, you not only protect yourself but also contribute to community immunity. Herd immunity reduces the spread of infectious diseases and protects vulnerable individuals who may not be able to receive vaccines due to health reasons.
Stay informed about recommended vaccinations for your age, health condition, and travel plans. Keep records of your immunizations and follow your healthcare provider’s guidance regarding vaccine schedules and booster doses to ensure ongoing protection.
Enhancing your immune system involves adopting a multifaceted approach that includes maintaining a balanced diet, staying hydrated, getting sufficient sleep, managing stress, practicing good hygiene, exercising regularly, limiting alcohol consumption, maintaining a healthy weight, and staying up-to-date with vaccinations.



Post Comment